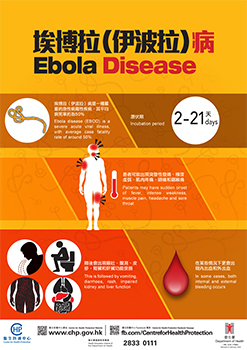
The Ebola disease (EBOD) is caused by infection with Ebola virus which belongs to the family Filoviridae. The incubation period ranges from 2 to 21 days. Patients may have sudden onset of fever, intense weakness, muscle pain, headache and sore throat. This is followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash, impaired kidney and liver function, and in some cases, both internal and external bleeding. EBOD outbreak in humans has an average case fatality rate of around 50% (varied from 25% to 90% in previous outbreaks).
The virus is introduced into the human population through close contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other body fluids of infected animals. It then spreads in the community through human-to-human transmission, with infection resulting from direct contact (through broken skin or mucous membranes) with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected people, and indirect contact with environments contaminated with such fluids. Although rare, sexual transmission of the EBOD has been reported.
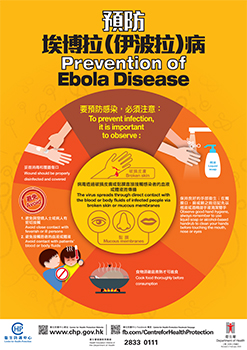
There is currently no registered vaccine for EBOD in Hong Kong. To prevent the infection, it is important for travellers who go to affected areas to observe the following:
- Observe good personal and environmental hygiene, always remember to use liquid soap or alcohol-based handrub to clean your hands before touching the eyes, nose and mouth
- Avoid close contact with feverish or ill persons, and avoid contact with blood or bodily fluids of patients, including items which may have come in contact with an infected person's blood or bodily fluids
- Avoid contact with animals
- Cook food thoroughly before consumption
For details, please refer to the factsheet of Ebola Disease.
For other languages [हिन्दी (Hindi), नेपाली (Nepali), اردو (Urdu), ไทย (Thai), Bahasa Indonesia and Tagalog], please click here
 |
 |
|
||||||||||||